KLH Dataset II » History » Revision 24
« Previous |
Revision 24/34
(diff)
| Next »
Eric Hou, 07/23/2010 10:51 AM
Public Data Sets: KLH2¶
KLH Dataset II: 655 defocus pairs of micrographs, coordinate centers of ~10000 side-view particles, a preliminary 3D reconstruction.
1. Images.¶
Images were acquired with a FEI Tecnai F20 equipped with a 2Kx2K CCD Tietz camera, as defocal pairs at a nominal magnification of 62,000 x and a voltage of 120 KeV, using the Leginon system (Potter et al., 1999; Carragher et al., 2000). The first image (named *.001.mrc) is acquired at near to focus (NTF) conditions (-0.6 to -1.5 µm) and the second image (named *.002.mrc) at farther from focus (FFF) conditions (-3µm). The time interval between the two exposures is approximately 20s due to the time required to read out the digital image from the camera. The pixel size is 2.2Å at the specimen scale and the accumulated dose for each high magnification image area was ~10 e/Ų.
Below is an example of a defocus pair. Click on the images to see at full scale.
(a)  (b)
(b) 
(a) Near to focus - NTF image. (b) Far from focus - FFF image.
Figure 1: An example pair of high magnification images of KLH.
Downloading High Magnification Images
Image files are provided in MRC format and as JPEG files
Download entire set of images using a tool called Dbemwiz, and use section name "02oct09a".
3. Coordinates of the Picked Particles in the Images¶
Since the NTF image in a defocus pair covers almost the same specimen area as the FFF image, the relative distance between particles within the NTF image should be the same as that in the FFF image. Using phase correlation, we are able to accurately align the NTF image to the FFF image in a defocus pair (Zhu et al., 2001). Therefore particles in the NTF image can be then extracted using the positions of the particles selected in the FFF image shifted according to the results of the alignment. We provide in the following only the positions of particles automatically selected in the FFF images.
(a)  (b)
(b) 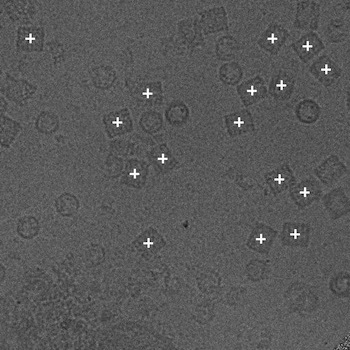
(a) The NTF image. (b) The FFF image.
Figure 3: An example pair of images outlined with particles selected by Selexon. Each "+" indicate a detected particle.
As we mentioned in the introduction, particle picking is an open, unresolved problem. Even for biological experts, the final picks may vary from person to person. Besides posting the particles picked by our own program Selexon, we will also post other manual/automated picks upon available. For each set of picked particles, we give a brief description of the criteria for manual picks, or the algorithm for automated picks. Links to more detailed descriptions will be provided when available.
Table 1: Positions of Manual Picked Particles.
| Picker | Brief Description of the Algorithm | Links to download |
| Selexon | A two-stage framework is developed for automatic selection of KLH particles. Under this framework, a cryoEM image is first decimated to generate a much smaller sized image with a coarser resolution but increased signal-to-noise ratio. Candidate particles in the decimated image are detected using edge and contour information, particularly the Hough transforms (Zhu et al., 2003). Afterwards, candidate particles in the original full resolution image are extracted by projecting the coordinates of particles in images with a coarser resolution. The candidate particles are then subject to a second stage of processing-pruning false alarms. In this stage, correlation based template matching method is applied to effectively reject low-quality particles or junk, using templates generated by aligning and averaging the candidate particles. With this two-stage framework, computational efficiency is achieved through the coarse-to-fine strategy while the high accuracy relies in the refinement in the second stage. Time required for picking side view KLH particles depends on the number of particles in an image, but is roughly 1 minute per image. | Coordinates of 11309 side-view particles selected in the FFF images. |
4. Sample 3D Reconstructions¶
Table 2: Sample reconstructions generated using particles listed above.
| Picker | Three-dimensional Density Map (click on the images to download the map) | Description of Reconstruction Procedures | Comments |
| Selexon |   |
A D5 point-group symmetry was imposed. The series of 10997 particles was subjected to several cycles of 3D projection alignment, using a previous volume as a reference, and a new reconstruction volume was calculated. | Coordinates of 10997 side-view particles went into the map. |
5. References ¶
- Carragher, B., Kisseberth, N., Kriegman, D., Milligan, R. A., Potter, C. S., Pulokas, J., and Reilein, A. (2000) Leginon: An automated system for acquisition of images from vitreous ice specimens. J. Struct. Biol. 132: 33-45.
- Potter, C. S., Chu, H., Frey, B., Green, C., Kisseberth, N., Mad-den, T. J., Miller, K. L., Nahrstedt, K., Pulokas, J., Reilein, A., Tcheng, D., Weber, D., and Carragher, B. (1999) Leginon: A system for fully automated acquisition of 1000 micrographs a day. Ultramicroscopy 77: 153-161.
- Zhu, Y., B. Carragher, D. Kriegman, R. Milligan, and C. Potter (2001) Automated Identification of Filaments in Cryo-electron Microscopy Images. J. Struct. Biol. 135: 302-312.
- Zhu, Y., Carragher, B., and Potter, C. S. (2003) Automatic Particle Detection Through Efficient Hough Transforms. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging 22(9): 1053-1062.
Updated by Eric Hou over 15 years ago · 34 revisions